Why
to implement Data Warehousing?
1.
To
perform server/ disk bound tasks associated with query and reporting on server
/ disks not used by transaction processing system.
It means,
Every organization has different
databases for Transactions, Query and Reporting purpose.
This is because, if they generate
reports on the Transactional Database, it will be varying for every hour.
And if transaction Database
stores huge amount of data, then perform select will consume more time and also
it will internally affect transaction process.
Hence
they can't exactly analyze the up's and Down's of their Business.
But if they perform the Query and
Generate reports on static data which varies less frequently, they can analyze
their business in better way.
This is the main reason for
Evaluation of Data Warehousing.
2.
To
use data models and/ or server technologies that speed up query processing and
reporting which are not appropriate for transaction processing.
There are several techniques to
speed up the query process like Star Schema, Using Clusters, Bit map indexing
etc.. But All of them effect the performance of DML operations on the data. Hence
if they are implemented on the transactional database, entire database process
will be collapsed.
There a few more server technologies which
improves transaction processing but reduces the query and reporting process. Hence the Organizations or firms started using
Data Warehouse for separating the business logic from data to data transaction
process.
3.
To
provide an environment where a relatively small amount of knowledge of the
technical aspects of database technology is required to write and maintain
queries and reports and/ or to provide a means to speed up the writing and
maintaining of queries and reports by technical personnel.
4.
To
provide a repository of "Cleaned Up" transaction processing system
data that can be reported against and that doesn't necessarily require fixing
the transaction processing systems.
5.
To
make it easier, on a regular basis to query and report data from multiple
transaction processing systems and/ or from external data that must be stored
for Query / Report purposes only.
6.
To
provide a repository of transaction processing system data that consists data
from a longer span of time than can efficiently be held in a transaction
processing system and/ or to be able to generate reports " As Was" as
of a previous point in time.
7.
To
prevent persons who only need to query and report transaction processing system
data from having any access whatsoever to transaction processing system
databases and logic used to maintain those databases.
Example:
In
order to store data over the years, many application designers in each branch
have made their individual decisions as to how an application and database
should be built. So source systems will be different in naming conventions,
variable measurements encoding structures, and physical attributes of data.
Consider
a bank that has got several branches in several countries, has millions of
customers and the lines of business of the enterprise are savings, and loans. The
following example explains how the data is integrated from source systems to
target systems.
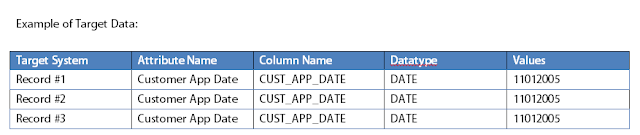
In the aforementioned example, attribute name, column name, datatype and values are entirely different from one source system to another. This inconsistency in date can be avoided by integrating the data into a data warehouse with good standards.
In the above example of target data, attribute name, column name, and datatypes are consistent throughout the target system. This is how data from various is integrated and accurately stored into the data warehouse.

No comments:
Post a Comment